Binary Tree
A binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, referred to as the left child and the right child.
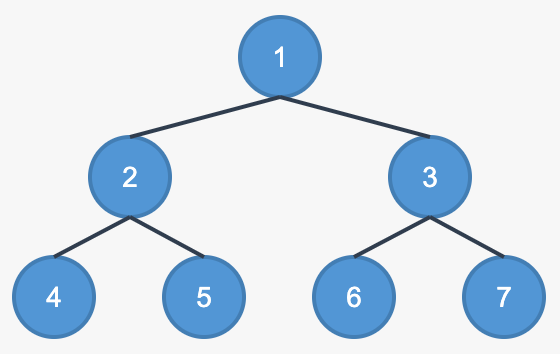
B-Tree
A B-tree is a self-balancing tree data structure that maintains sorted data and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. It is optimized for systems that read and write large blocks of data.
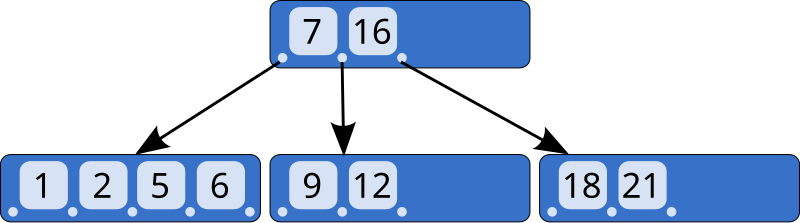
B+ Tree
A B+ tree is an extension of a B-tree, optimized for systems that read and write large blocks of data. In a B+ tree, all keys and data are stored in the leaf nodes, while internal nodes only store keys for guiding the search.
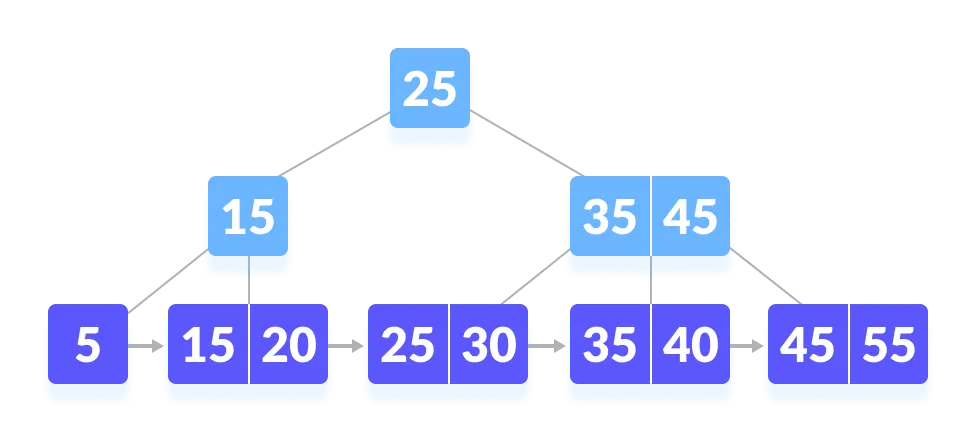
MySQL InnoDB: Bidirectional linked list
B+ Tree Time Complexity
Search Operation
- Time Complexity: O(log n)
- Explanation: In a B+ tree, search involves traversing from root to leaf
- The height of the tree is logarithmic to the number of elements
Insertion Operation
- Time Complexity: O(log n)
- Includes search time to find the correct leaf node
- May involve splitting nodes if they’re full
Deletion Operation
- Time Complexity: O(log n)
- Includes search time to find the element
- May involve merging or redistributing nodes
Range Query
- Time Complexity: O(log n + m)
- Where ’m’ is the number of elements in the range
- Efficient due to linked leaf nodes
Space Complexity
- O(n) where n is the number of elements
Key Points:
- B+ trees maintain balance, ensuring consistent performance
- High fanout reduces tree height, improving efficiency
- Leaf nodes linked for fast sequential access