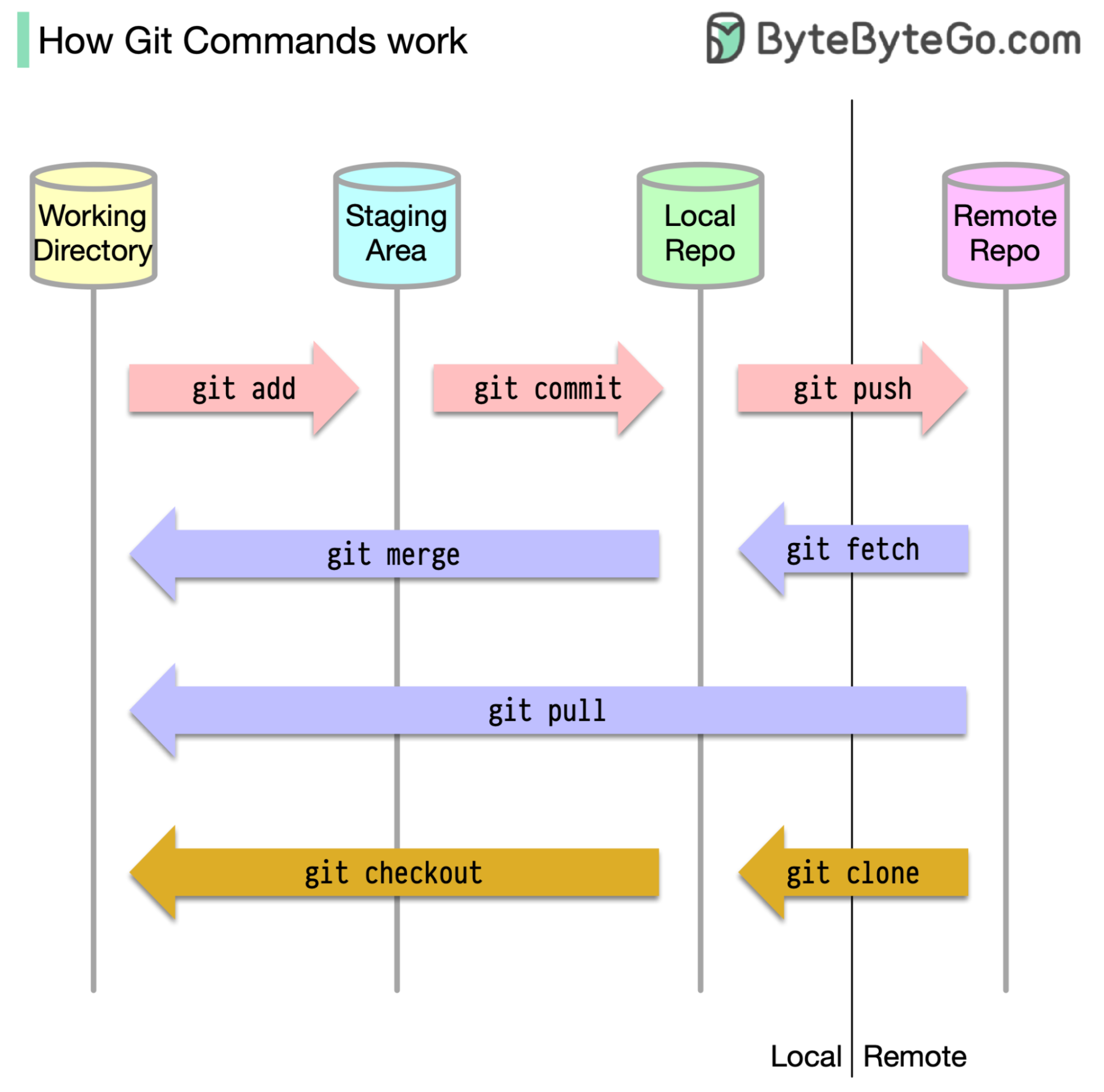
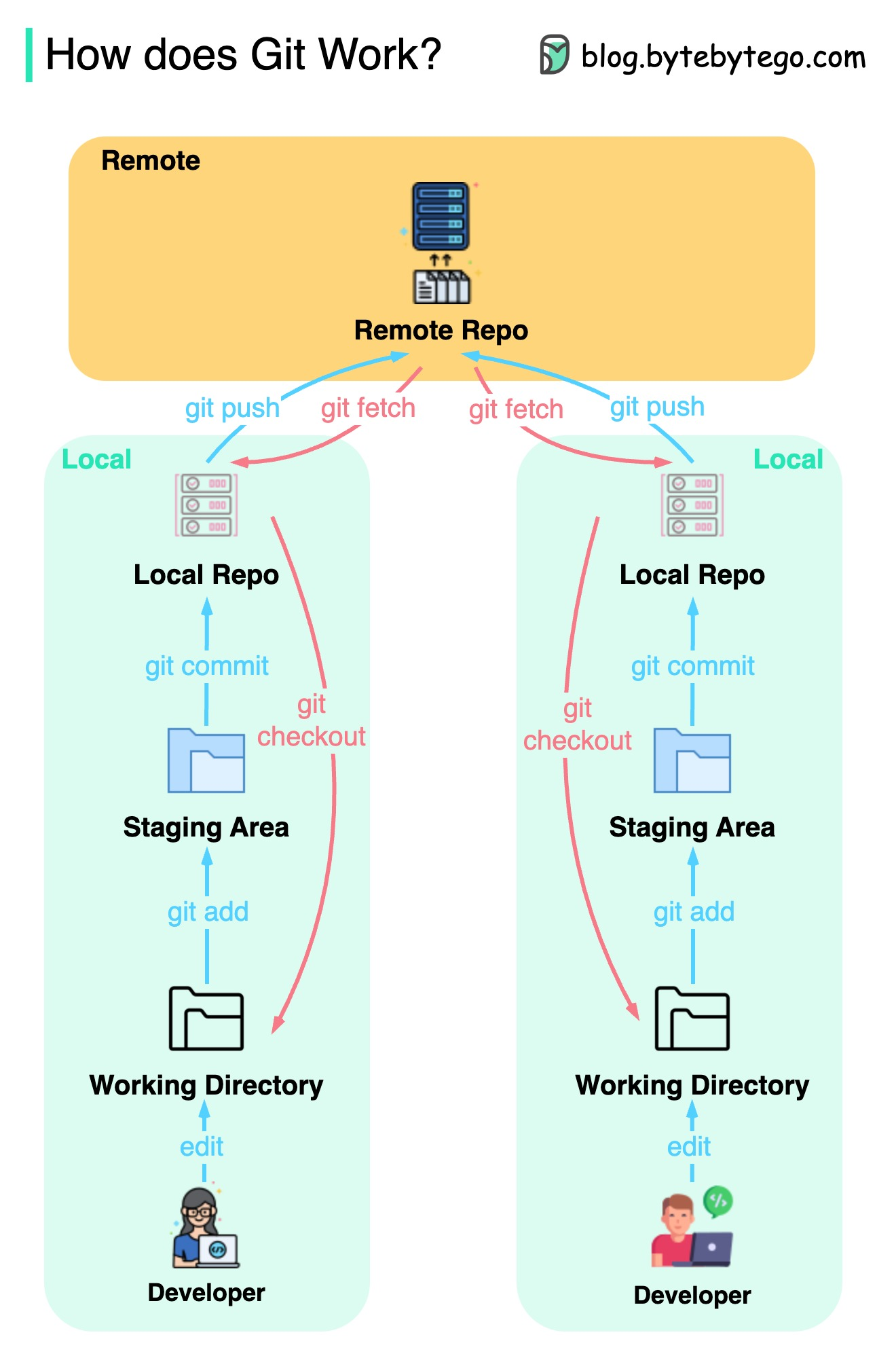
GIT CHEAT SHEET
CREATE
- Clone an existing repository:
$ git clone ssh://user@domain.com/repo.git - Create a new local repository:
$ git init
LOCAL CHANGES
- Changed files in your working directory:
$ git status - Changes to tracked files:
$ git diff - Add all current changes to the next commit:
$ git add . - Add some changes in
<file>to the next commit:$ git add -p <file> - Commit all local changes in tracked files:
$ git commit -a - Commit previously staged changes:
$ git commit - Change the last commit (do not amend published commits!):
$ git commit --amend
COMMIT HISTORY
- Show all commits, starting with the newest:
$ git log - Show changes over time for a specific file:
$ git log -p <file> - Who changed what and when in
<file>:$ git blame <file>
BRANCHES & TAGS
- List all existing branches:
$ git branch -av - Switch HEAD branch:
$ git switch <branch> - Create a new branch based on your current HEAD:
$ git branch <new-branch> - Create a new tracking branch based on a remote branch:
$ git checkout --track <remote/branch> - Delete a local branch:
$ git branch -d <branch> - Mark the current commit with a tag:
$ git tag <tag-name>
UPDATE & PUBLISH
- List all currently configured remotes:
$ git remote -v - Show information about a remote:
$ git remote show <remote> - Add new remote repository, named
<remote>:$ git remote add <shortname> <url> - Download all changes from
<remote>, but don’t integrate into HEAD:$ git fetch <remote> - Download changes and directly merge/integrate into HEAD:
$ git pull <remote> <branch> - Publish local changes on a remote:
$ git push <remote> <branch> - Delete a branch on the remote:
$ git push <remote> --delete <branch> - Publish your tags:
$ git push --tags
MERGE & REBASE
- Merge
<branch>into your current HEAD:$ git merge <branch> - Rebase your current HEAD onto
<branch>(do not rebase published commits!):$ git rebase <branch> - Abort a rebase:
$ git rebase --abort - Continue a rebase after resolving conflicts:
$ git rebase --continue - Use your configured merge tool to solve conflicts:
$ git mergetool - Use your editor to manually solve conflicts and (after resolving) mark file as resolved:
$ git add <resolved-file> $ git rm <resolved-file>
UNDO
- Discard all local changes in your working directory:
$ git reset --hard HEAD - Discard local changes in a specific file:
$ git checkout HEAD <file> - Revert a commit (by producing a new commit with contrary changes):
$ git revert <commit> - Reset your HEAD pointer to a previous commit…and discard all changes since then:
$ git reset --hard <commit> - …and preserve all changes as unstaged changes:
$ git reset <commit> - …and preserve uncommitted local changes:
$ git reset --keep <commit>